
Ramén Valves, 28 November
What to consider when choosing automation for control valves
Choosing automation for control valves is a critical decision that can significantly impact the cost, efficiency, reliability, and safety of industrial processes.
Here are some key factors to consider when making this decision:
Process Requirements:
Understand the specific requirements of your process, including flow rates, pressure ranges, temperature ranges, and the type of fluid being controlled. This will help determine the appropriate type and size of control valve and the level of automation needed.
Valve Type:
Different control valve types, such as globe, ball, butterfly, and rotary valves, have varying characteristics and performance capabilities. Choose a valve type that aligns with your process requirements and performance expectations.
Control Accuracy and Range:
Determine the required control accuracy and range for your application. Some processes demand very precise control, while others may have wider acceptable ranges.
Automation Type:
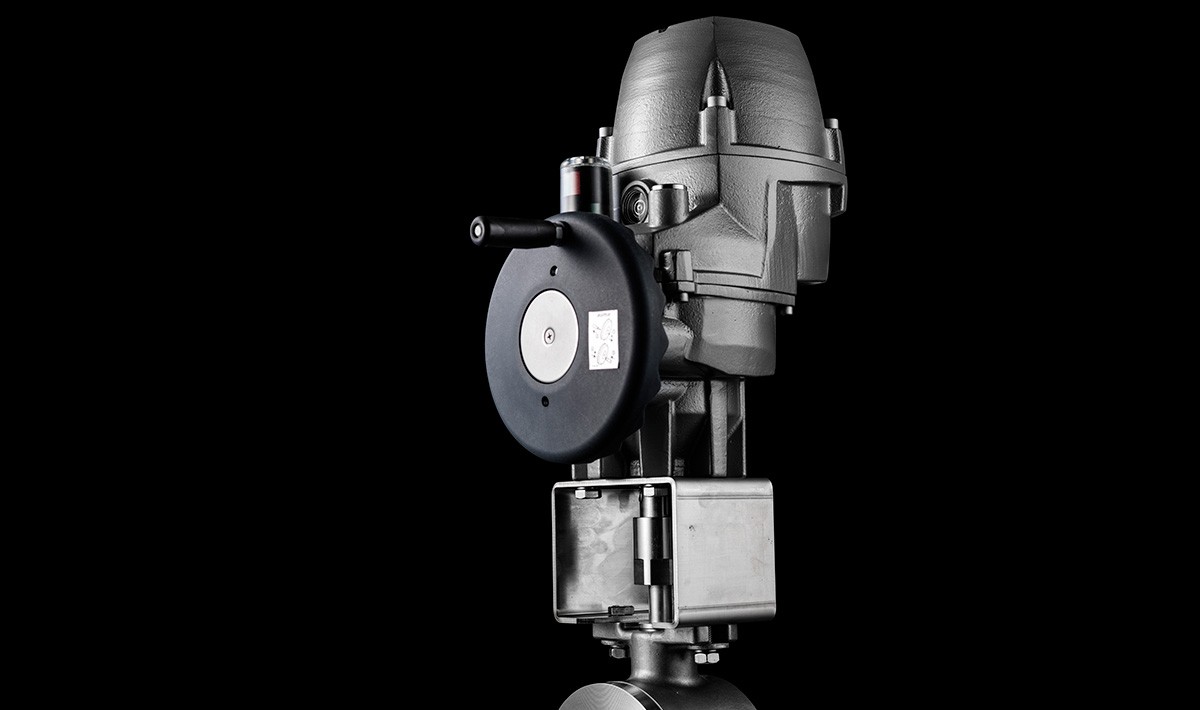
Decide on the level of automation needed, ranging from basic manual control to fully automated systems. This includes choices such as pneumatic, electric, or digital valve controllers. Hand level is the simpliest way.
Communication Protocols:
Consider the communication protocols required for integrating the control valves into your process control system. Common protocols include HART, Foundation Fieldbus, PROFIBUS, and Modbus. Most common is a 4-20 mA control loop.
Safety and Reliability:
Prioritize safety and reliability. Choose automation systems and components that adhere to industry standards and have a track record of reliable performance.
Maintenance and Serviceability:
Evaluate the ease of maintenance and serviceability of the chosen automation solution. Components should be easily accessible for maintenance and replacement without disrupting the entire process. A bracket, between the valve and the actuator, is needed when an actuator cannot or should not be mounted directly onto the valve. Direct mount is less maintenance friendly, can cause valve leakage to damage the actuator.
Environmental Conditions:
Consider the environmental conditions in which the control valves will operate, including temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to corrosive or hazardous materials.
Power Source:
Determine the power source available for the automation system, whether it’s pneumatic, electric, or another source. Ensure that the power source is compatible with the chosen automation technology. Older control systems may have voltage output and not 4-20 mA that is std today. This may require special adapters.
Integration with Control System:
Ensure that the chosen automation solution can seamlessly integrate with your existing process control system or can be easily integrated if you are implementing a new system.
Lifecycle Costs:
Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including initial purchase, installation, maintenance, and potential downtime costs. Sometimes, investing more upfront in a higher-quality automation solution can result in lower long-term costs.
Supplier Support:
Choose a reputable supplier or manufacturer that offers strong technical support, training, and readily available spare parts. Preferable local support in your language.
Future Expandability:
Consider whether the chosen automation solution allows for future expansion or upgrades as your process requirements evolve.
Regulatory Compliance:
Ensure that the chosen control valve automation solution complies with relevant industry standards, regulations, and safety codes. Consider CE marking as mandatory. ATEX, SIL and others may be applicable depending on the usage and installation.
User Interface and Monitoring:
Evaluate the user interface and monitoring capabilities of the automation system. User-friendly interfaces and remote monitoring capabilities can greatly improve operational efficiency.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision when choosing automation for control valves that best suits your process needs and contributes to the overall success of your operations.
 Language
Language Swedish
Swedish English
English
